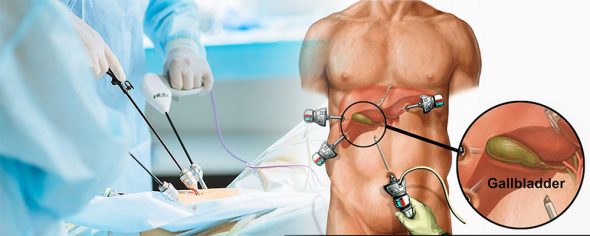
Laparoscopic biliary surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat various conditions affecting the bile ducts, gallbladder, and sometimes the liver. This procedure involves the use of a laparoscope—a thin tube equipped with a camera and light—that allows surgeons to view the internal organs on a high-definition monitor. The surgery is performed through small incisions, typically less than an inch in size, through which the laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The precision offered by the laparoscopic approach makes it particularly effective in treating biliary conditions while minimising damage to surrounding tissues. This method is widely used for gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), bile duct exploration, and the treatment of bile duct injuries or strictures.
This surgical technique has gained popularity due to its minimal recovery time and reduced complications compared to traditional open surgery.
Here we discuss laparoscopic biliary surgery and its key aspects to help you understand why it is often the preferred choice for many patients.
Common Conditions Treated by Laparoscopic Biliary Surgery
- Gallstones
One of the most frequent reasons for undergoing laparoscopic biliary surgery is the presence of gallstones. These small, hard deposits can form in the gallbladder and cause significant pain and complications if left untreated. Gallstones can block the bile ducts, leading to infections or pancreatitis. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the standard procedure for removing the gallbladder and the stones within it. The surgery is quick, with most patients being discharged on the same day or the day after.
- Bile Duct Injuries and Strictures
Injuries to the bile ducts, often resulting from previous surgeries, or strictures (narrowing of the bile ducts) can cause bile to leak into the abdomen or lead to jaundice and infections. Laparoscopic biliary surgery can repair these injuries or remove blockages, restoring normal bile flow and reducing the risk of further complications.
- Biliary Dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia is a condition where the gallbladder does not empty properly, leading to pain and digestive issues. This surgery is sometimes recommended to remove the gallbladder, providing relief from symptoms and preventing further problems.
How the Procedure Works
The laparoscopic biliary surgery procedure is simple but requires a high degree of skill from the surgical team.
- Preparation: The patient is placed under general anaesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free during the surgery. Once anaesthetised, the surgical team will sterilise the area and make several small incisions in the abdomen.
- Insertion of the Laparoscope: A laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions. The camera on the laparoscope provides a magnified, high-definition view of the biliary system on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see the area in detail.
- Surgical Instruments: Additional instruments are inserted through the other incisions. These tools are used to manipulate the organs, remove the gallbladder, repair bile ducts, or remove any obstructions.
- Completion: Once the procedure is completed, the instruments are removed, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape. The patient is then moved to a recovery area where they are monitored as they wake up from anaesthesia.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Biliary Surgery
There are several reasons why laparoscopic biliary surgery has become the preferred choice for treating biliary conditions:
- Minimally Invasive Approach
The small incisions used in the surgery result in less trauma to the body. This means less pain for the patient, fewer wound complications, and a reduced risk of infection. Additionally, the smaller incisions lead to less scarring, which is a significant cosmetic benefit for many patients.
- Faster Recovery Time
Most individuals can return to normal activities within a week or two, as opposed to several weeks with open surgery. This quicker recovery time also means a shorter hospital stay, with many patients being discharged within 24 hours.
- Lower Risk of Complications
With laparoscopic biliary surgery, the risk of complications such as bleeding and infections is significantly lower. The precision of the laparoscope allows surgeons to operate with greater accuracy, reducing the likelihood of accidental damage to surrounding organs.
Possible Risks and Complications
While the surgery is generally safe, it is important to be aware of the potential risks. Complications are rare but can include:
- Infection
Although the risk is lower compared to open surgery, there is still a possibility of infection at the incision sites. Proper post-operative care, including keeping the wounds clean and following the surgeon’s instructions can minimise this risk.
- Bleeding
Surgeons are highly skilled at controlling bleeding during surgery, but patients should be aware of the signs of post-operative bleeding, such as excessive bruising or swelling.
- Injury to Surrounding Organs
The precision required in the surgery means that the risk of injuring surrounding organs, such as the intestines or liver, is very low. However, it is still a potential risk, and patients should discuss these concerns with their surgeon.
Recovery Process and Aftercare
- Post-Operative Care
After the surgery, patients will be monitored in a recovery room until the effects of anaesthesia wear off. Most patients are discharged within 24 hours, though some may stay longer depending on the complexity of the surgery and their overall health.
- Pain Management
Some discomfort is normal after surgery, but this can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions regarding medication and avoid any strenuous activities during the first week of recovery.
- Dietary Adjustments
After laparoscopic biliary surgery, particularly if the gallbladder has been removed, patients may need to make temporary dietary changes. A low-fat diet is often recommended initially to allow the digestive system to adjust.
- Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the healing process and ensure there are no complications. During these visits, the surgeon will check the incision sites, assess the patient’s recovery, and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic biliary surgery is a highly effective and minimally invasive option for treating a variety of biliary conditions. Its benefits, including smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery times, make it a preferred choice for both patients and surgeons. Whether you’re facing gallbladder removal or treatment for bile duct injuries, this surgery offers a safe and efficient solution. Trust the expertise and care provided by hospitals likes BLK-Max Hospital to guide you through your surgery and recovery, ensuring the best possible outcome for your health.